New NASA Model Finds Landslide Threats in Near Real-Time During Heavy Rains
Special Stories
29 Mar 2018 8:14 PM
From NASA
For the first time, scientists can look at landslide threats anywhere around the world in near real-time, thanks to satellite data and a new model developed by NASA.
The model, developed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, estimates potential landslide activity triggered by rainfall. Rainfall is the most widespread trigger of landslides around the world. If conditions beneath Earth's surface are already unstable, heavy rains act as the last straw that causes mud, rocks or debris — or all combined — to move rapidly down mountains and hillsides.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E6LaojSkZQQ
The model is designed to increase our understanding of where and when landslide hazards are present and improve estimates of long-term patterns. A global analysis of landslides over the past 15 years using the new open source Landslide Hazard Assessment for Situational Awareness model was published in a study released online on March 22 in the journal Earth's Future.
"Landslides can cause widespread destruction and fatalities, but we really don’t have a complete sense of where and when landslides may be happening to inform disaster response and mitigation," said Dalia Kirschbaum, a landslide expert at Goddard and co-author of the study. "This model helps pinpoint the time, location and severity of potential landslide hazards in near real-time all over the globe. Nothing has been done like this before."
The model estimates potential landslide activity by first identifying areas with heavy, persistent and recent precipitation. Rainfall estimates are provided by a multi-satellite product developed by NASA using the NASA and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission, which provides precipitation estimates around the world every 30 minutes. The model considers when GPM data exceeds a critical rainfall threshold looking back at the last seven days.
In places where precipitation is unusually high, the model then uses a susceptibility map to determine if the area is prone to landslides. This global susceptibility map is developed using five features that play an important role in landslide activity: if roads have been built nearby, if trees have been removed or burned, if a major tectonic fault is nearby, if the local bedrock is weak and if the hillsides are steep.
If the susceptibility map shows the area with heavy rainfall is vulnerable, the model produces a "nowcast" identifying the area as having a high or moderate likelihood of landslide activity. The model produces new nowcasts every 30 minutes.
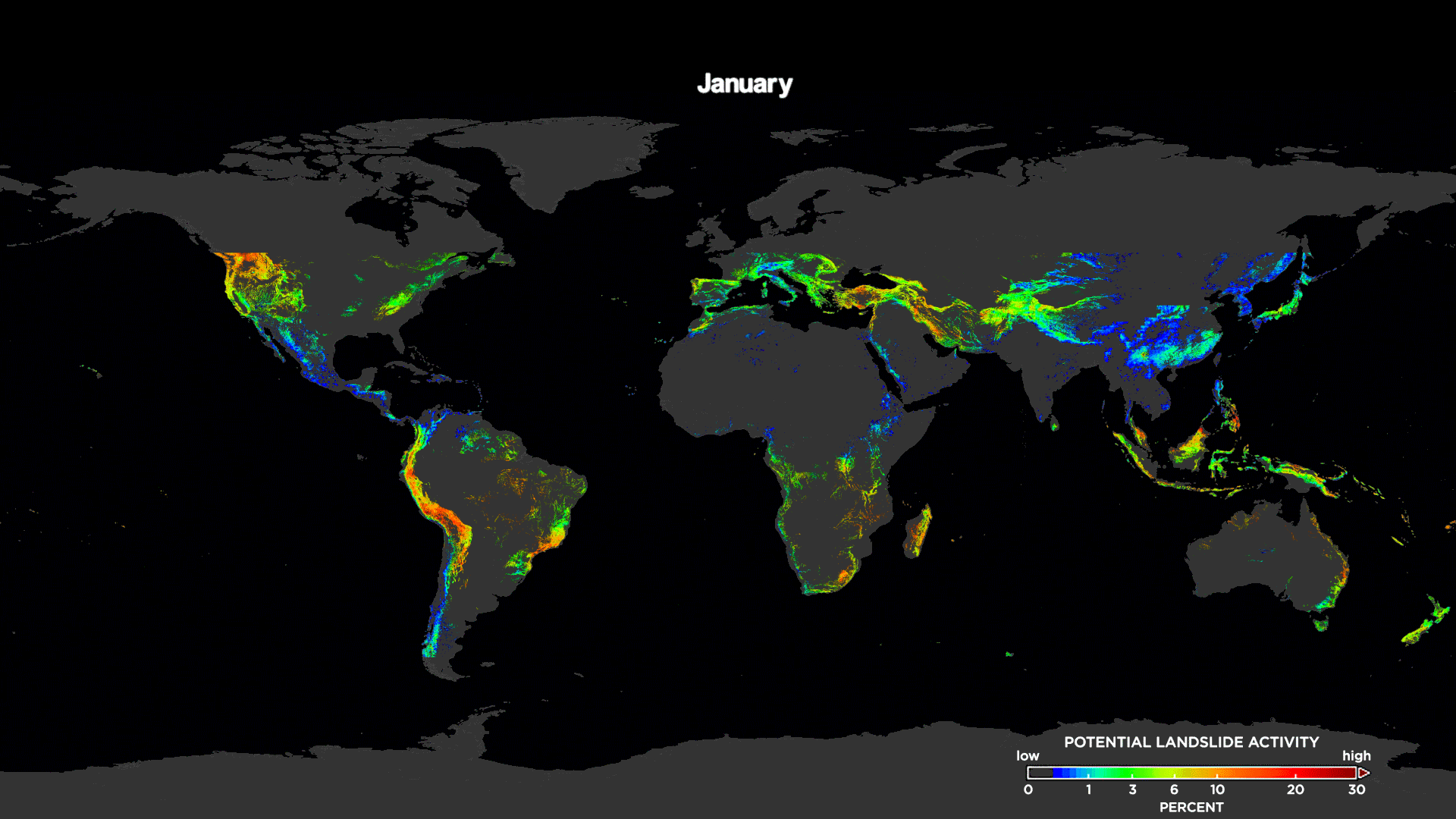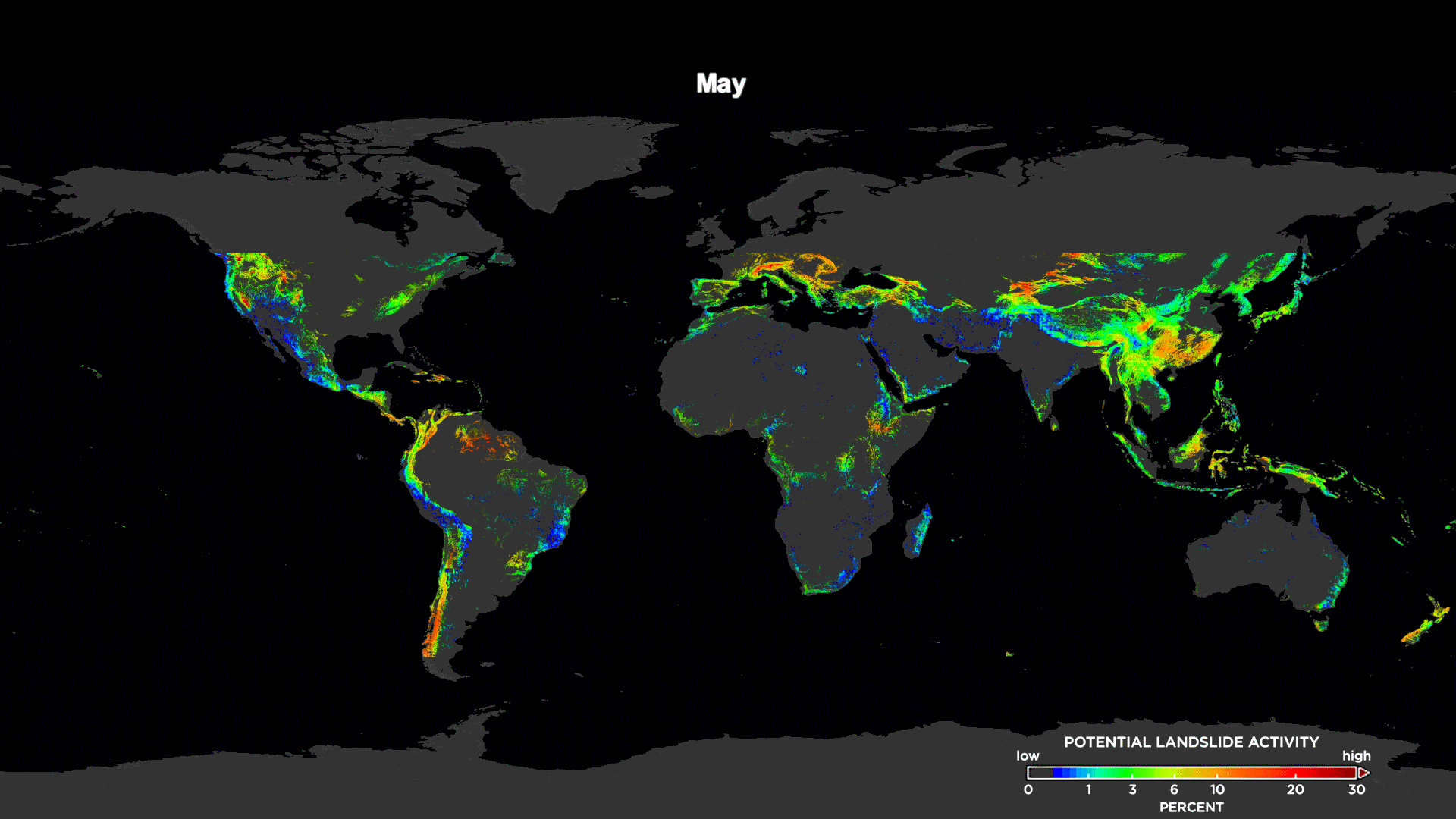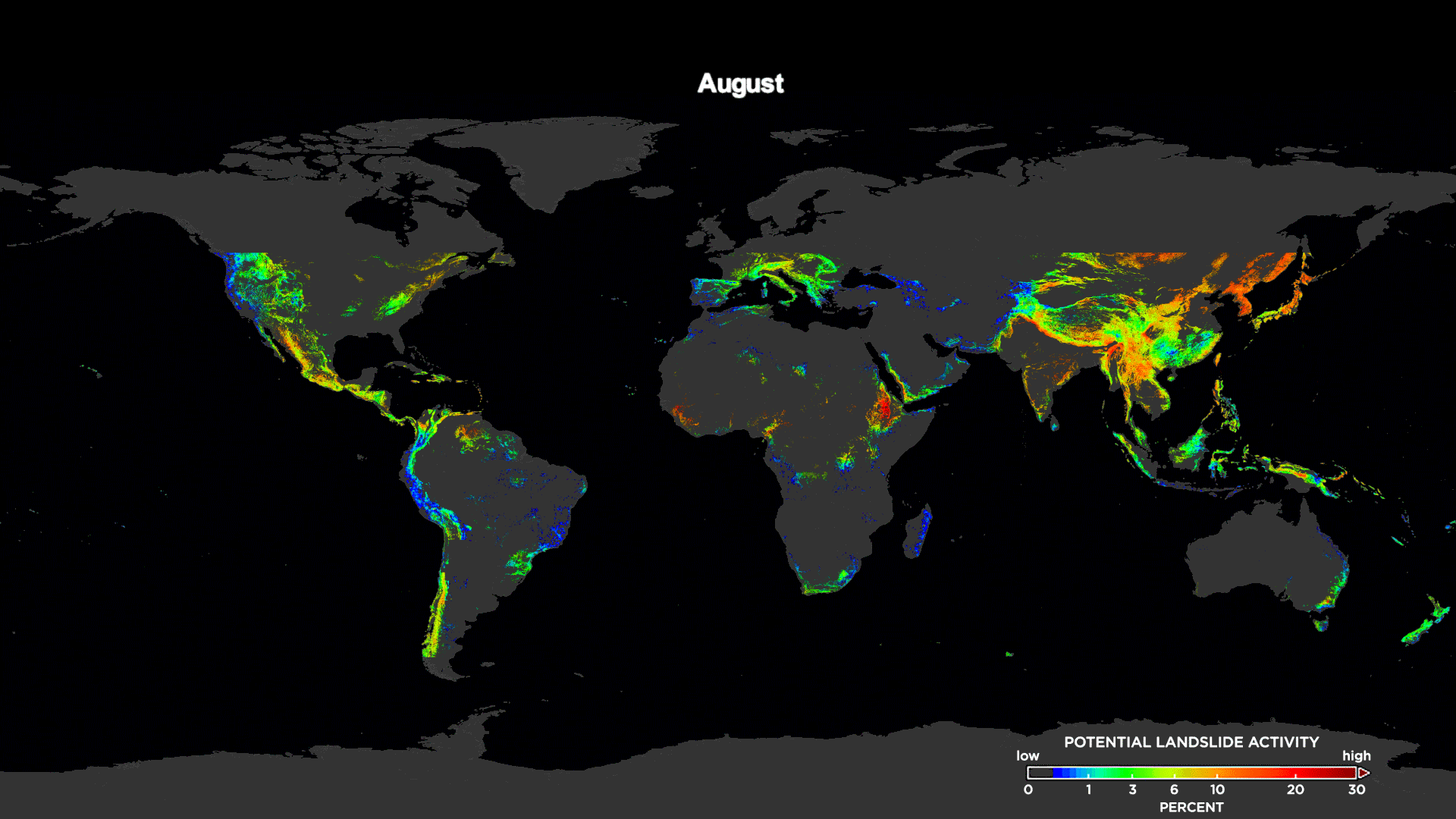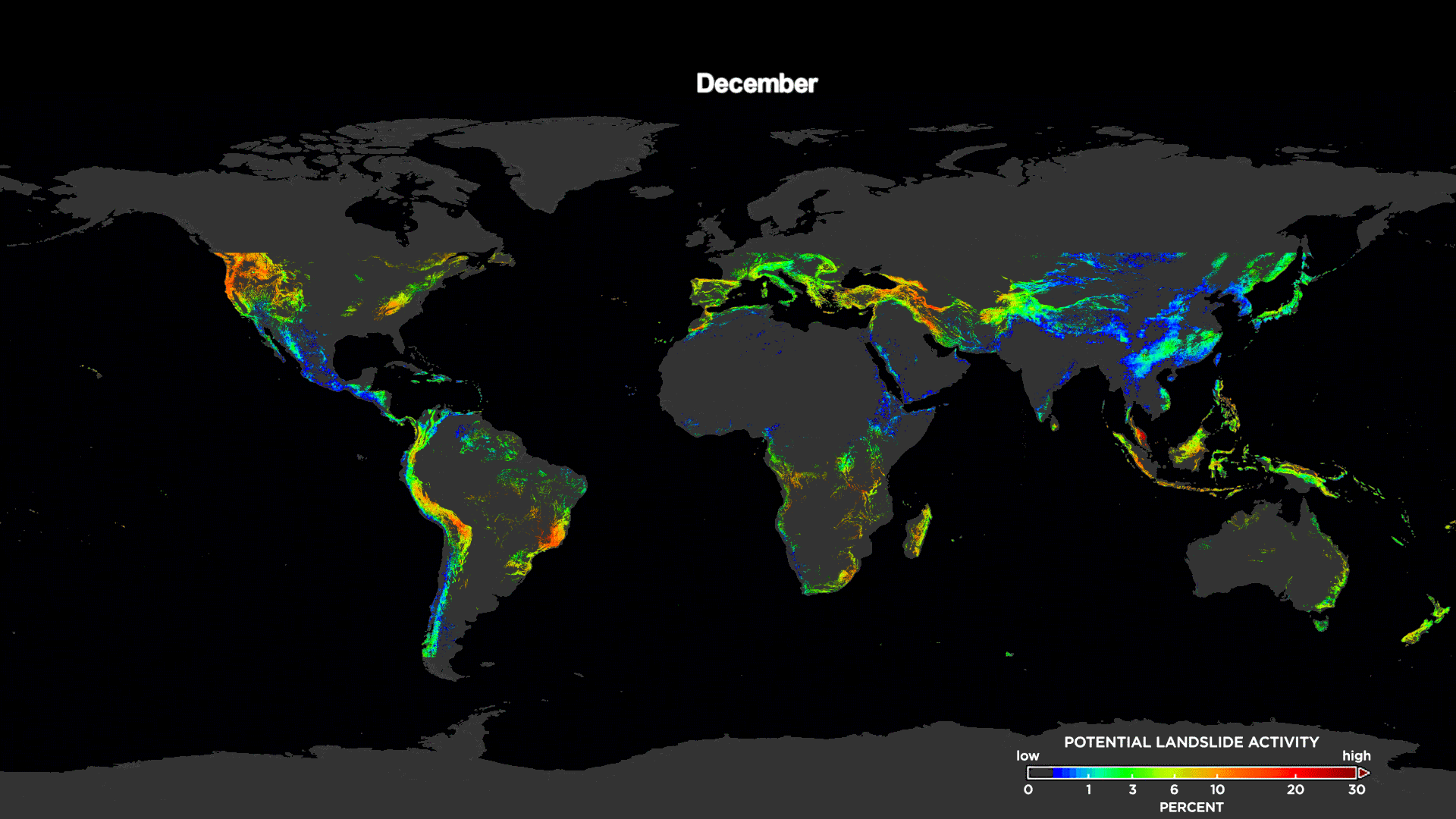

[This animation shows the potential landslide activity by month averaged over the last 15 years as evaluated by NASA's Landslide Hazard Assessment model for Situational Awareness model. Here, you can see landslide trends across the world. Credits: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center / Scientific Visualization Studio]
The study shows long-term trends when the model's output was compared to landslide databases dating back to 2007. The team’s analysis showed a global "landslide season" with a peak in the number of landslides in July and August, most likely associated with the Asian monsoon and tropical cyclone seasons in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
"The model has been able to help us understand immediate potential landslide hazards in a matter of minutes," said Thomas Stanley, landslide expert with the Universities Space Research Association at Goddard and co-author of the study. "It also can be used to retroactively look at how potential landslide activity varies on the global scale seasonally, annually or even on decadal scales in a way that hasn't been possible before.
Edited for WeatherNation by Meteorologist Mace MichaelsAll Weather News
More